Car Bus | Detailed Introduction to Ethernet
foreword
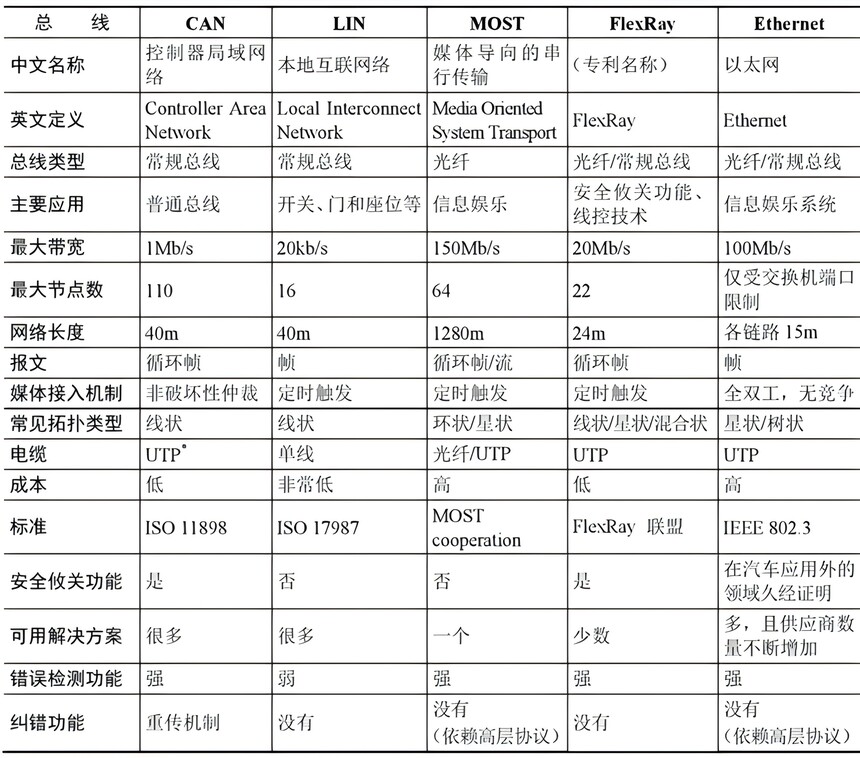
Previously, CAN, CAN FD, LIN, FlexRay, and MOST buses were introduced. This article introduces the in vehicle Ethernet.
The corresponding articles are as follows:
CAN bus: Car bus | Detailed introduction of CAN
CAN FD bus: Car bus | Detailed introduction of CANFD
LIN bus: Vehicle bus | Detailed introduction of LIN
FlexRay Bus: Vehicle Bus | Detailed Introduction to FlexRay
Summary of commonly used car buses: Car bus | Understanding the five major car buses in one article: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, MOST, Ethernet

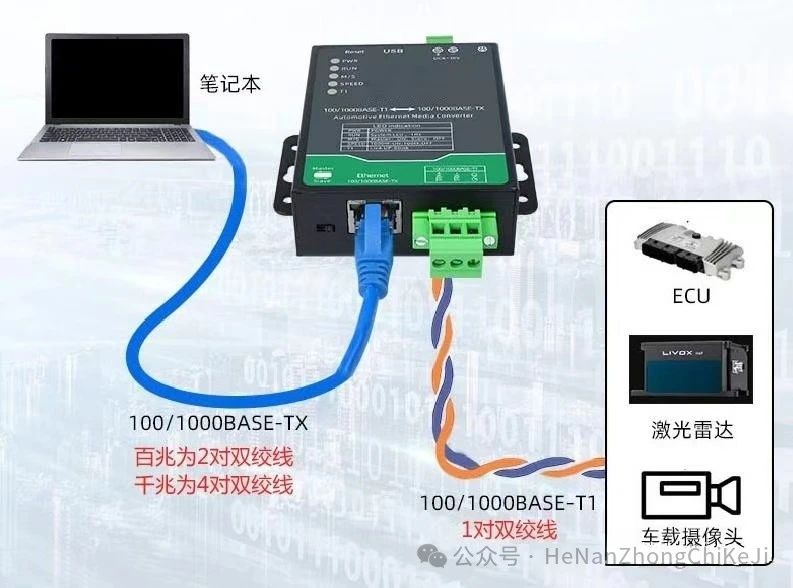

The first stage mainly involves the promotion and application of the DoIP protocol for on-board diagnostic systems and ECU software refresh, as well as the use of IP cameras in driving assistance systems. DoIP (IP based diagnostic communication) allows vehicles to perform diagnostic communication through IP networks, which is an example of early applications of in vehicle Ethernet.
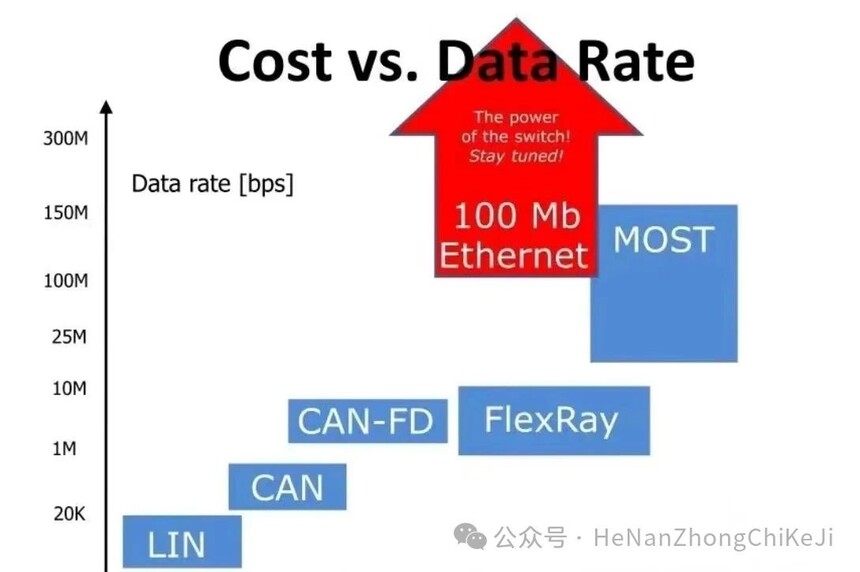
High speed transmission: The data transmission rate of vehicle Ethernet can reach 100Mbit/s to 1Gbit/s, or even higher, far exceeding the traditional CAN bus's 8Mbps.
High reliability: Vehicle Ethernet can resist harsh environments inside the vehicle, including vibration, temperature changes, and electromagnetic interference.
Low latency: For autonomous driving and real-time safety systems, onboard Ethernet provides deterministic and low latency communication.
Real time synchronization: The onboard Ethernet supports precise time synchronization, which is crucial for coordinating multiple electronic control units (ECUs) and sensors in the vehicle.
Easy to expand: With the increase of vehicle functions, in car Ethernet can be easily expanded to support more devices and sensors.
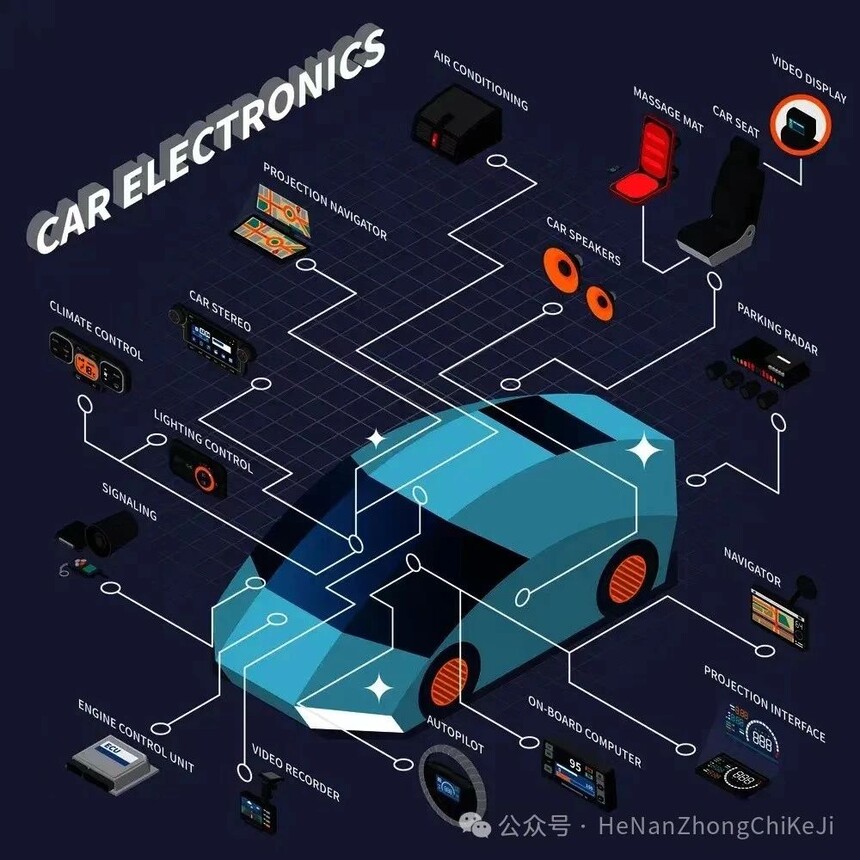
GPS devices: Connected to GPS devices via Ethernet in vehicles, providing accurate vehicle positioning information is crucial for vehicle navigation, route planning, and future autonomous driving functions.
Mobile devices: Through on-board Ethernet, smart phones and other mobile devices can be seamlessly connected with the vehicle system to achieve the control of the infotainment system, telephone calls, SMS processing and Internet access.
Video sensors: High definition cameras and video sensors are important components of modern automotive safety systems, including reversing cameras, surround view systems, and forward collision warning systems in ADAS systems. Vehicle Ethernet can transmit a large amount of data generated by these sensors.
In car infotainment system: The in car Ethernet provides sufficient bandwidth to support high-definition video and audio streams, enhancing the entertainment experience for both drivers and passengers.
V2X communication: Communication between vehicles and other vehicles (V2V), infrastructure (V2I), pedestrians (V2P), and networks (V2N) is crucial for improving road safety and traffic efficiency. Vehicle Ethernet can support these communication requirements.
Diagnostic tool: The onboard Ethernet also supports remote diagnosis and software updates, which are crucial for vehicle maintenance and upgrades.


推薦
-

-

QQ空間
-

新浪微博
-

人人網
-

豆瓣

