Components | One article takes you through the concept of "resistors" in components“
Electronic components are a general term for components and devices.
Electronic components: such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc. that do not generate electrons themselves and have no control or conversion effect on voltage and current, known as "passive devices"
Electronic devices: such as transistors, diodes, field-effect transistors, integrated circuits, etc., which can generate electrons themselves and have control and conversion effects on voltage and current, known as "active devices"
Common electronic components: resistors, capacitors, diodes, field-effect transistors, transistors, power chips, crystal oscillators, CPUs, communication chips, converters, driver chips, light-emitting diodes, optocouplers, transformers, relays, motors, filters, tactile switches, etc.
Zhongchi will explain commonly used electronic components in stages for everyone. In this issue, let's learn about resistors together.
resistance

Resistance, commonly abbreviated as R, is a fundamental property of a conductor that is related to its size, material, and temperature. It is the most commonly used component in electronic circuits. The main physical characteristic of resistance is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy, which can also be said to be an energy consuming component. When current passes through it, internal energy is generated. Resistors usually play a role in dividing and diverting voltage in circuits. For signals, both AC and DC signals can pass through resistors.
The domestic resistor model consists of four parts
1. Main name, using letters to represent the product name. For example, W represents potentiometer, R represents resistance
2. Material, using letters to indicate what material the resistor is made of. For example: X-ray winding, T-carbon film, S-organic solid, J-metal film, Y-oxide film, C-deposited film, H-synthetic carbon film, I-glass glaze film.
3. Classification, generally represented by numbers, individual types are represented by letters, and the corresponding types are represented by numbers/letters. For example: 1/2- ordinary, 3- ultra-high frequency, 4- high resistance, 5- high frequency, 6/7- precision, 8- high voltage, 9- special, G - high power, T - adjustable.
4. Serial number, using numbers to represent different varieties of similar products, used to distinguish the product's external dimensions and performance indicators.
Resistors can be divided into fixed resistors, variable resistors, and special resistors according to their structure
Resistors can be divided into square chip resistors, cylindrical resistors, long strip integrated resistors, and tubular wound resistors according to their appearance
Resistors can be divided into carbon film, metal film, metal oxide film, wire wound resistor, and SMT surface mount resistor according to their materials
Resistors are classified according to their purpose
Resistors classified by material

Metal film precision resistor
Metal film precision resistor: It uses high-temperature vacuum coating technology to tightly attach nickel chromium or similar alloys to the surface of ceramic rods to form a film. After cutting and adjusting the resistance value, it achieves the final required precision resistance value. Then, it is cut with appropriate joints and coated with epoxy resin for sealing protection on its surface.
Metal film resistors can adjust their resistance values by adjusting the material composition, film thickness, and grooves.
Characteristics of metal film precision resistors: good performance, small size, high precision, good temperature characteristics, low noise, high stability
Application of Metal Film Resistors: Home Appliances, Wireless Communication Equipment, Instrumentation, Military Aerospace and Other Fields with High Precision Requirements
Ⅱ. Carbon film resistor

Carbon film resistor: It is a type of thin film resistor, also known as "thermally decomposed carbon film resistor". It uses high-temperature vacuum coating technology to tightly attach carbon to the surface of the magnetic rod to form a carbon film, perform appropriate joint cutting, and apply epoxy resin sealing protection on the surface.
The thickness of the carbon film determines the resistance value, and the resistor is usually controlled by controlling the thickness of the film and the groove.
Characteristics of carbon film resistors: low price, high power, negative temperature coefficient resistor (temperature rise, resistance decrease), good stability, low accuracy (around ± 5%)
Application of Carbon Film Resistors: Not Suitable for High Precision Use Environments

Metal oxide film resistor: A fixed value axial resistor is made by vacuum evaporation or sputtering of metal oxide films such as tin oxide on ceramics or glass.
The resistance of metal oxide film resistors can be adjusted by adjusting the material composition, film thickness, and groove.
Characteristics of metal oxide film resistors: heat resistance, high stability, high reliability, noise potential (maximum noise of 0.2 μ V/V), temperature coefficient (± 300ppm/℃), standard capacitance deviation (± 5%), available tolerances (± 1%, ± 2%, ± 5%, ± 10%), resistance value (1 Ω~10M Ω), excellent high surge current
The application of metal oxide film resistors: used in control equipment that requires high stability in use environments, medical equipment, telecommunications, and power automation.

Wire wound resistor: also known as "wire wound resistor", is composed of a resistance wire (usually made of nickel chromium, manganese copper and other alloys with a certain resistivity) wound around an insulating skeleton (made of ceramic, plastic, metal coated with insulation layer, etc., in the form of a tube, flat, etc.).

SMD surface mount resistor: a fixed chip resistor, which is a type of metal glass glazed resistor. A resistor made by mixing metal powder and glass glaze powder and printing them on a substrate using screen printing method.
Features of SMD surface mount resistors: moisture resistance, high temperature resistance, strong anti-interference performance, good high-frequency characteristics, small temperature coefficient
SMD surface mount resistor applications: computers, mobile phones, medical electronic products, cameras, electronic meters
Structure classification resistor
Ⅰ. Fixed resistor

Fixed resistor: a basic component made of materials that have a blocking effect on current, where the resistance value of a fixed resistor remains constant or changes negligible.
Fixed resistor classification: carbon film resistor, metal film resistor, wire wound resistor, fuse resistor, cement resistor

Fuse resistor: a dual function component that normally has resistance characteristics. When a circuit fails and exceeds its rated power, it will melt and open for a certain period of time.
Classification of Fused Resistors:
Classified by working mode: repairable fuse resistor, irreparable fuse resistor
Classified by resistor material used: film type fuse resistor, wire wound fuse resistor, power type glazed wire wound resistor
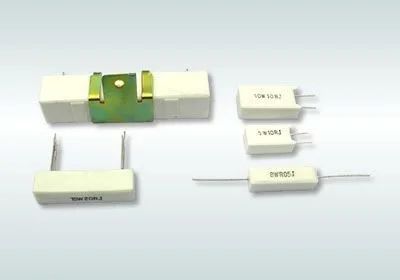
cement resistor
Cement resistor: It is a type of wire wound resistor, in which the resistance wire is wound on a non alkaline heat-resistant ceramic piece, protected and fixed with heat-resistant, moisture resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials on the outside, and the wound resistor body is placed in a ceramic frame, filled and sealed with special resin heat-resistant cement.
Classification of Cement Resistors: Ordinary Cement Resistors and Cement Wire wound Resistors.
Application of Cement Resistors: Computer Switching Power Supply, Automotive Circuits, Industrial Instruments, Power Adapter, Audio Divider

Adjustable resistor: a variable resistor whose resistance value can be manually adjusted to meet circuit requirements.
Classification of Adjustable Resistors: Fine tuning Resistors, Potentiometers

Commonly used fine-tuning resistors

potentiometer
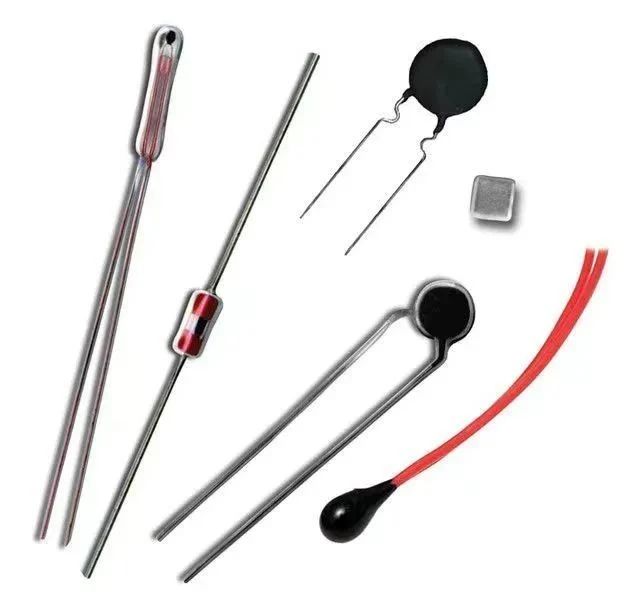

Thermistor: A temperature sensitive protective element composed of semiconductor ceramic materials, whose resistance value changes with temperature. Thermistors can be divided into positive temperature coefficient thermistors and negative temperature coefficient thermistors based on their temperature coefficients.
Positive temperature coefficient resistor: The resistance value increases with the increase of temperature
Negative temperature coefficient resistor: The resistance value decreases with increasing temperature
Characteristics of Thermistors: High sensitivity (temperature coefficient of resistance is more than 10-100 times higher than that of metals, able to detect temperature changes of 10-6 ℃), small size, good stability, strong overload capacity, wide working range (suitable for normal temperature devices -55 ℃~315 ℃; suitable for high temperature devices above 315 ℃ (currently up to 2000 ℃); suitable for low temperature devices -237 ℃~55 ℃), easy to process

Varistor: Varistor is a type of voltage limiting protective device. By utilizing the nonlinear characteristics of varistors, when overvoltage occurs between the two poles of the varistor, the varistor can clamp the voltage to a relatively fixed value, thereby achieving protection for the subsequent circuit.
Characteristics of Varistors: Non polarized, parallel voltage limiting protection device in the circuit, strong surge withstand capacity (up to 75KA), fast response speed (generally not exceeding 25NS), wide voltage range (generally from 18V~1800V), mainly used for low-frequency signal line protection, with multiple sizes.

Photoresistor: It is a resistor that changes with the intensity of external light. Special resistors made of semiconductor materials such as cadmium sulfide or cadmium selenide work based on the internal photoelectric effect.
The incident light intensity of the photoresistor decreases, the resistance decreases, the incident light is weak, and the resistance increases.
Types of photoresistors:
Classified by semiconductor materials: intrinsic photoresistors, doped photoresistors (with stable function, good characteristics, and wide applications)
According to the spectral characteristics of photoresistors:
Infrared photoresistor (containing photoresistors such as lead sulfide and lead telluride, used in missile guidance, infrared spectroscopy, infrared communication, national defense, scientific research, and industrial and agricultural production)
UV photoresistor (active in response to ultraviolet radiation, used for exploring ultraviolet radiation)
Visible light photoresistor (used in photoelectric automatic control circuits, navigation beacon lights, street lamps, active lighting systems, photoelectric active switch portals, photoelectric calculators).
The application of photoresistors: generally used for light measurement, light control, and photoelectric conversion; Such as street lights, corridor light control lights, smoke alarm lights.

Humidity sensitive resistor: an electronic component that can sense the humidity of the surrounding environment and change its own resistance value. Composed of moisture sensitive materials, insulation materials, and metal electrodes, the moisture sensitive material is the core component.
The resistance value of a humidity sensitive resistor varies with changes in environmental humidity.
Classification of humidity sensitive resistors: semiconductor ceramic humidity sensitive components, lithium chloride humidity sensitive resistors, organic polymer film humidity sensitive resistors
Applications of humidity sensitive resistors: meteorological observation, home appliance control, agricultural production, food storage, healthcare (ventilators, nebulizers)

Force sensitive resistor
Force sensitive resistor: It is a special component that converts mechanical energy into electrical signals. When pressure is applied to a semiconductor, it causes deformation and changes the symmetry inside the crystal. This is achieved through the pressure resistance effect of semiconductor materials, where the resistance value changes with the magnitude of external force.

gas sensitive resistor
Gas sensitive resistor: a sensor that converts detected gas components and concentrations into electrical signals, made by using certain semiconductors to absorb a certain gas and send an oxidation reaction, mainly composed of metal oxides.
Classification of gas sensitive resistors: metal oxide gas sensitive resistors, composite oxide gas sensitive resistors, ceramic gas sensitive resistors.
Application of Gas Sensing Resistors: Gas Sensing Detector
Resistors classified by appearance

Surface mount resistor: A fixed resistor made by mixing metal powder and glass glaze powder and printing them on a substrate using screen printing. It is currently a widely used electronic component, divided into two types: thin film resistors (generally used in linear circuits) and thick film resistors (generally using screen printing technology).
Advantages and disadvantages of surface mount resistors:
Advantages of thin film resistors: temperature stability, extremely low current noise, minimal nonlinear effects, and relatively easy precision control
Disadvantages of thin film resistors: low integration and high limitations
Advantages of thick film resistors: low cost, wide application
Disadvantages of thick film resistors: lower precision, temperature stability, and current noise compared to thin film resistors
Identification on surface mount resistors: "Conventional 3-digit labeling method", "Conventional 4-digit labeling method", "3-digit multiplier code labeling method", "R represents decimal point position", "m represents decimal point position"
Conventional 3-digit annotation method: XXY format, XXY=XX * 10Y, where XX represents a 2-digit significant number and Y represents a power of 10. Commonly used in the E-24 series.

Conventional 4-digit annotation method: XXXY format, XXXY=XXX * 10Y, where XXX represents a 3-digit significant number and Y represents a power of 10. Commonly used in the E-24 and E-96 series.

3-digit multiplier code annotation method: XXY format, where XX represents the code for significant numbers and needs to be converted into scientifically calculated numerical values; Y refers to the code of several powers of 10, which needs to be converted into scientific calculations of several powers of 10. Commonly used E-96 series.



、



Color ring resistors can be divided into "four ring resistors" and "five ring resistors" that have one more ring than the four ring resistors, usually using four ring resistors.
The basic units of color ring resistance are ohms (Ω), kiloohms (K Ω), and megaohms (M Ω)
Four loop resistor: The first two loops are numbers, the third loop represents the multiplication of the resistance value, and the last loop represents the error.
Five ring resistor: The first three rings are numbers, the fourth ring represents the multiplication of the resistance value, and the last ring represents the error.
Note: Errors are usually represented by gold (representing resistance error ± 5%), silver (representing resistance error ± 10%), brown (representing resistance error ± 1%), colorless (representing resistance error ± 20%), and occasionally green (representing resistance error ± 0.5%)

Resistance color ring meter
Color ring chart memory rhyme:

色环电阻对应色环表示例图
Color ring resistor identification reading method:

Four color ring resistor: a resistor represented by a four-color ring, counting from left to right, with the first color ring indicating the highest resistance value; The second color ring represents the second digit of the resistance value; The third color ring represents the multiplication of the resistance value; The fourth color ring represents the allowable deviation of the resistance value.
Example: A four loop resistor has a green first loop (representing 5), a purple second loop (representing 7), a yellow third loop (representing 10K times), and a gold fourth loop (representing ± 10% error); If 57 * 10000=570K Ω, then the resistance value of the four ring resistor is 570K Ω, and the error range of the resistance value is ± 10%

Five color ring resistor: a resistor represented by a five color ring, counting from left to right, with the first color ring indicating the highest resistance value; The second color ring represents the second digit of the resistance value; The third color ring represents the third digit of the resistance value; The fourth color ring represents the multiplication of the resistance value; The fifth color ring represents the allowable deviation of the resistance value.
Example: A five colored ring resistor, with the first ring being red (representing 2), the second ring being green (representing 5), the third ring being orange (representing 3), the fourth ring being silver (representing 0.01 times), and the fifth ring being brown (representing resistance error ± 1%); That is, 253 * 0.01=2.53 Ω, indicating that the resistance value of the five ring resistor is 2.53 Ω, with an error range of ± 1%
Small tips for identifying order:
(1) First, find the color ring that indicates the resistance error. Commonly used colors to represent resistance error are gold, silver, and brown; Among them, gold and silver are rarely used as the first ring of the resistance color ring. Therefore, if there is a gold/silver ring in the resistor, it can be basically considered as the last ring of the color ring resistor.
(2) Is the brown ring an error marker for discrimination. The brown ring is often used as both an error ring and a significant digit ring, often appearing simultaneously as the first and last rings, making it difficult to distinguish which side is the first ring. In practice, judgment can be made based on the interval between color rings according to experience. The first few rings are almost close and equidistant, while the last ring is relatively far away from the previous one. The following figure can be used as a reference.
Addendum:
Six color ring resistor identification method: counting from left to right, the first color ring is the digit with the highest resistance value; The second color ring represents the second digit of the resistance value; The third color ring represents the third digit of the resistance value; The fourth color ring represents the multiplication of the resistance value; The fifth color ring represents the allowable deviation of the resistance value, and the sixth color ring represents the temperature coefficient of the resistor.

Note: Six color ring resistors are only used in electronic products with specific requirements, and are generally used very rarely. A brief understanding is sufficient.
Color ring identification is mainly used on cylindrical resistors, such as carbon film resistors, color ring resistors, metal film resistors, fuse resistors, winding resistors, metal oxide film resistors, etc.
按用途分类的电阻器

推薦
-

-

QQ空間
-

新浪微博
-

人人網
-

豆瓣

