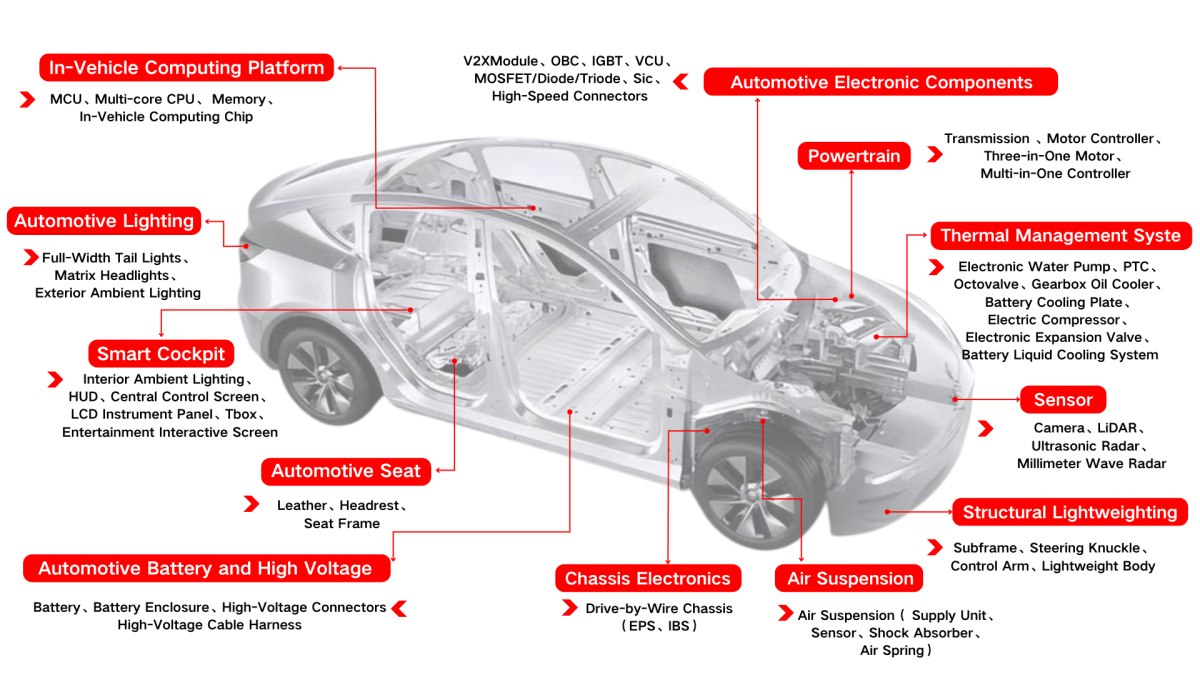
2024-11-07
With the innovative development of the new four modernizations of automobiles (interconnectivity, automation, sharing, and electrification), the number and types of chips used in vehicles are constantly increasing. This article introduces the chip types that play a key role in modern cars: MCU microcontroller unit (MCU) is an indispensable component of automotive electronic systems, responsible for controlling and managing various functions and systems of the car. Application of MCU: 1 Engine control: MCU is used to control fuel injection, ignition timing, emission control, etc. to improve fuel efficiency and performance. 2. Vehicle electronic system: including window control, car lock, interior lighting, air conditioning system, etc. The MCU is responsible for executing user instructions and automatic control. 3. Safety systems: such as Anti lock Braking System (ABS), Traction

2024-11-07
Introduction to Field Effect Transistor (FET) Field effect transistor, abbreviated as FET, is a semiconductor device that uses electric field effect to control current. Unlike traditional bipolar transistors (BJTs), FETs are only conducted by majority carriers (electrons or holes), hence they are called unipolar transistors. 2、 The working principle of FET field-effect transistor is mainly composed of three regions: gate, drain, and source. In normal operating conditions, the gate voltage controls the current between the source and drain, thereby achieving control over the field-effect transistor. Cut off state: When the gate voltage is lower than the threshold voltage, there is no conductive channel between the gate and the channel, and electrons cannot flow from the drain to the source. The field-effect transistor is in a cut off state, equivalent to an insulator. Conduction status:

2024-11-07
1、 Understanding of Transistors 1.1 Understanding of Commonly Used Transistors (1) Meaning: The full name of a transistor is a "crystalline transistor", also known as a "transistor". It is a typical semiconductor component. The three poles of a transistor: base (b): used to activate the transistor collector (c): the positive pole of the transistor (collecting charge carriers) emitter (e): the negative pole of the transistor (emitting charge carriers) base current controls the current between the collector and emitter. (2) Types ① Common transistors can be mainly divided into two categories based on their polarity structure: NPN type and PNP type. PNP transistor: composed of two series connected crystal diodes. NPN transistor: Basically used to amplify weak signals into strong signals According to different power levels, transistors can be divided into low power, medium power, and high power. Low power transistor, low power transistor power P

2024-11-07
1、 Understand diode 1 What is a diode? A diode is a commonly used semiconductor device, which is composed of a P-N junction formed by a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor, with corresponding electrode leads led out at both ends of the P-N junction, and sealed with a tube shell. 2. Common structures of diodes: (1) Point contact type: small junction area, small junction capacitance, so the allowed current of the junction is small, and the highest operating frequency is high. (2) Surface contact type: With a large junction area and capacitance, the junction allows for a high current and a low maximum operating frequency. (3) Flat type: The junction area can be small or large, with small junctions having high operating frequencies and large junctions allowing for large currents. 3. Classification of diodes There are many types of diodes, and according to their actual functions, common diodes can be divided into rectifier diodes, voltage regulator diodes, and detector diodes

2024-11-07
Electronic components are a general term for components and devices. Electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc., do not generate electrons themselves and have no control or transformation effect on voltage and current, known as "passive devices". Electronic components, such as transistors, diodes, field-effect transistors, integrated circuits, etc., can generate electrons themselves and have control and transformation effects on voltage and current, known as "active devices". Zhongchi will explain electronic components in stages. In this issue, let's learn about inductors together. Inductors, abbreviated as inductors, are made by winding wires (such as enameled wire, yarn wrapped wire, silver plated copper wire, etc.) in a single or multiple layers on an insulating tube. The letter "L" is commonly used in circuit diagrams. 1、 Types of inductors 1 Classified by appearance (1) Hollow inductor (hollow coil) ① Hollow coil is a type of wire wound coil

2024-11-07
Electronic components are a general term for components and devices. Electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc., do not generate electrons themselves and have no control or transformation effect on voltage and current, known as "passive devices". Electronic components, such as transistors, diodes, field-effect transistors, integrated circuits, etc., can generate electrons themselves and have control and transformation effects on voltage and current, known as "active devices". Zhongchi will explain electronic components in stages for everyone. In this issue, let's learn about capacitors together. Capacitor 1. Structure and Definition of Capacitor 1. The structure of a capacitor is composed of two metal electrodes sandwiching an insulating dielectric layer. 2. Definition of capacitor: In physics, a capacitor is a static charge storage substance. Capacitance/capacitance is a physical quantity that represents the ability of a capacitor to hold charge. Two pole pl

2024-11-07
Electronic components are a general term for components and devices. Electronic components: such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc., do not generate electrons themselves and have no control or transformation effect on voltage and current, known as "passive devices". Electronic components: such as transistors, diodes, field-effect transistors, integrated circuits, etc., can generate electrons themselves and have control and transformation effects on voltage and current, known as "active devices". Commonly used electronic components: resistors, capacitors, diodes, field-effect transistors, transistors, power chips, crystal oscillators, CPUs, communication chips, converters, driver chips, light-emitting diodes, optocouplers, transformers, relays, motors, filters, tactile switches, etc. Zhongchi will explain commonly used electronic components in stages for everyone. In this issue, let's learn about resistors together. 1. The meaning of resistance: Resistance is usually